Actually, ESS for South Korea.
Renewable Energy Followers 18th Jihoon Oh
When we get to talk about South Korea, geographical limit always stands. Geographical limit even stands as a risk when we do valuation for South Korean corporations. What would “Geographical limit” be?
South Korea lies in lat. 33˚ - 43˚; long. 124˚ - 132˚ of single climatic zone on northern hemisphere with the total area 100,364 km2 which is relatively small. Also, excluding the northern side, South Korea is surrounded by water on three sides, with flat land and mountains accounting for 30% and 70%, respectively. Mountains consist with 15% of mountains over 1000m above sea level while 65% of it is lower than 500m above sea level with the eastern part of the range rising higher than the western part. Because of these geographical features, South Korea would not be able to separate the risk of intermittent power generation resulting from various weather while countries with large area can. When weather affects the Korean Peninsula, South Korea may face serious power supply crisis if the national power generators are consisted with wind power and solar power only. Thus, since South Korea has developed its economy mainly through high-tech industries which has higher demand on electricity compared to other industries, the risk can be highly calculated.
On October 2021, University of California and Tsinghua College presented combined article, “Geophysical constraints on the reliability of solar and wind power worldwide” on NATURE well known worldwide. The article dealt issues assuming energy systems rely heavily on solar and wind resources, spatial and temporal mismatches between resource availability and electricity demand may result in negative consequences on system reliability. Through analyzing mixed renewable generation, varying hypothetical scale and energy capacity of 42 countries from 1980 to 2018, the team reanalyzed hourly data quantifying the power energy, and utilization rates of additional energy storage, demand management or curtailment and also regional aggregation. Under condition that there is perfect transmission and annual generation equal to annual demand but no energy storage, the most reliable renewable electricity systems are wind power satisfying countries’ electricity demand in 72–91% of hours (83–94% when adding 12 hours of storage). However, even when systems met over 90% of demand, the team pointed hundreds of hours of unmet demand may occur annually. In case for South Korea’s reliability over power system relying on wind power and solar power like shown on the graph above, share and hours of unmet electricity demand of the most reliable solar-wind systems assuming specified storage and generation quantities, South Korean reliability was calculated to be 72.2% which is lower than other countries such as Russia (90.9%), Canada (89.8%), Australia (89.5%), Egypt(88.2%), United States(87.7%) and China(87.5%). Additionally, like the graph below, most countries try to control power supply gap under 3 hours from yearly 8670 hours (99.97%) annually.
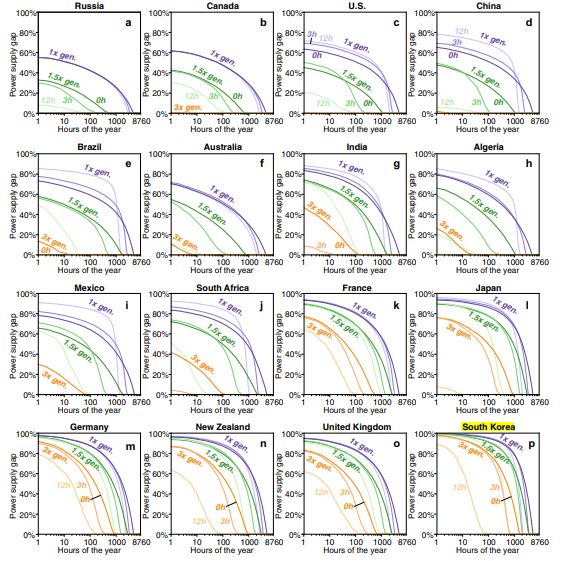
[Material 1. Global Average power supply gaps ]
출처 : NATURE
If power supply is covered by only solar and wind power with no energy storage which increases intermittence, South Korea may face lowered stability of electricity. However, when additional energy storage that can store electricity for 12 hours, South Korean power reliability increases from 72% to 86%.
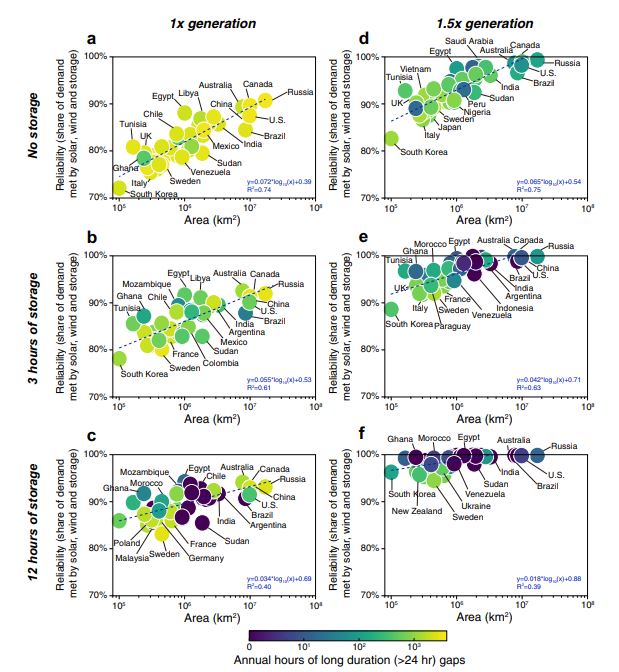
[Material 2. The relationship between the highest reliability of electricity supply system among 42 major countries]
출처 : NATURE
This is why we need ESS (Energy Storage System) in order to increase reliability of power system. ESS is like a large battery that can store electricity and use it when we need which is known to play essential role on stabilizing power supply and increasing efficiency.
Then let’s take a look at South Korean ESS market. on 2017, South Korean ESS market showed high increase by discounting electricity charge and increasing multiple of REC (Renewable Energy Certificate) favoring ESS companies. However, the market froze rapidly due to occurrence of 28 fire accidents from August 2017 to October 2019 with unresolved cause of the fire which amplified concerns with safety. Not only that, ESS companies faced financial difficulties due to operating losses due to abnormal operation, increased maintenance expenses following decreased demand over ESS. This increased a risk of investing on ESS industry resulting lower amount of investments. On the other hand, the global ESS market is gaining attention as a new growth engine, breaking away from the traditional power generation method, and many investments are being made through policies to encourage ESS implementation and open the power auxiliary service market.
With the expansion of the global ESS market, South Korea, which has played a leading role in the existing battery industry, needs to resolve the limitations of wind and solar power generation due to geographical factors and expand the ESS market for better future.
ESS 에 대한 대학생신재생에너지기자단 기사 더 알아보기
1. "한국의 지리학적 한계와 ESS", 18기 오지훈, https://renewableenergyfollowers.tistory.com/3547?category=745296
참고문헌
1) Dan Tong, David J. Farnham, Lei Duan, Qiang Zhang, Nathan S. Lewis, Ken Caldeira Steven J. Davis, "Geophysical constraints on the reliability of solar and wind power worldwide", 2021.10.22, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26355-z
3) 선정민, "태양광·풍력 입지… 한국, 42國중 꼴찌- 네이처, 주요국 분석 보고서", 조선일보, 2021.11.13 ,https://www.chosun.com/national/transport-environment/2021/11/13/FMJAEEZTGZDS7GGUHNBGXU2LGQ/
4) 이윤정, 연 44%씩 커지는 ESS 시장… 한국은 안전 논란·지원 미비로 ‘고사 위기’, 조선일보, 2021.11.15, https://biz.chosun.com/industry/company/2021/11/15/B5VC6CNYHJHVDBWKTVZJTT7H4Y/
5) 한국문화원, 한국소개-사회, https://www.koreanculture.org.au/ko/about-korea-society/


'News > 기술-산업-정책' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 공급망 ESG관리의 중요성, 혼자만 잘해서 되는게 아냐 (5) | 2021.12.05 |
|---|---|
| 탄소중립을 향한 보폭, 국제전력기술엑스포 BIXPO 2021! (5) | 2021.12.05 |
| 위기에 빠진 석유업계, 극복할 방안은? (2) | 2021.11.29 |
| 주류계도 작정했다, 위스키로 만든 친환경 연료 (7) | 2021.11.29 |
| 온실가스 감축목표 40%, 우리에게 던져진 과제는 무엇인가 (11) | 2021.11.29 |





댓글